The Security Debt of Vibe Coding: What I Found Auditing 12 Projects
I built 12 projects with AI assistance. Then I ran a security audit across all of them. The results were eye-opening — and every vibe coder needs to hear this.
By Mike Hodgen
The Dark Side of Building Fast
Vibe coding changed my life. In the last year, I've shipped more projects than most dev teams ship in three. SaaS tools, ecommerce platforms, booking apps, internal dashboards, API workers — all built with AI as my copilot.
But last week, I did something uncomfortable. I ran a real security audit across every project I've built. Not a quick npm audit. A full, systematic scan — dependency checks, secret scanning, header analysis, input validation review, auth middleware audit, rate limiting assessment.
I found 29 security issues across 12 projects. Some were critical.
Here's the thing: none of them were bugs AI introduced maliciously. They were gaps AI never thought to fill. And if you're building with AI the way I am, you probably have the same ones.
Why AI Doesn't Think About Defense
When you prompt an AI to build an API route, it gives you a working endpoint. Request comes in, response goes out. It works. Ship it.
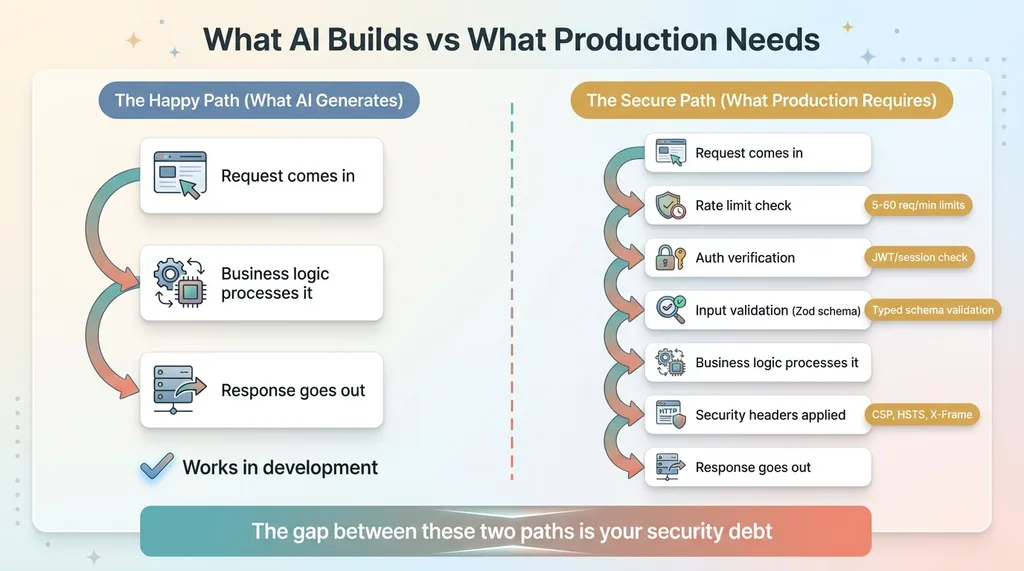 Happy Path vs Secure Path
Happy Path vs Secure Path
But "working" and "secure" aren't the same thing.
AI assistants optimize for the happy path. They build what you ask for. They don't volunteer:
- "Should we validate that request body before processing it?"
- "What happens if someone hits this endpoint 1,000 times per second?"
- "Did you add security headers to prevent clickjacking?"
- "Is that API key sitting in a file that's committed to git?"
These aren't exotic attack vectors. They're baseline security hygiene that every production app needs. Vibe coding skips them almost every time — not because the coder is careless, but because the feedback loop doesn't surface them.
Your app works. Users are happy. Nothing looks broken. The security debt just accumulates silently until someone finds it.
What I Found: The Big Five
I categorized every finding by type. Here's what showed up across a dozen production projects — SaaS apps, ecommerce tools, booking platforms, internal dashboards, and API workers.
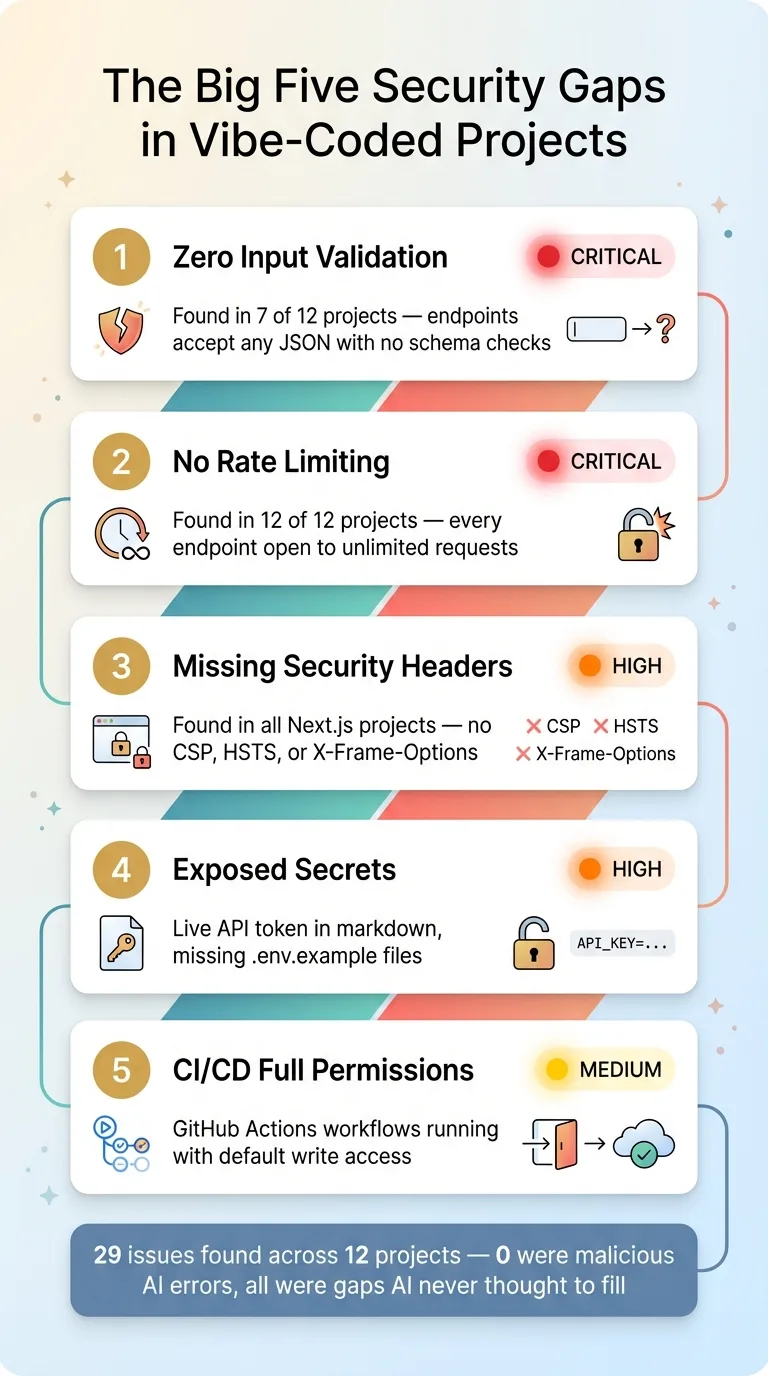 The Big Five Security Gaps
The Big Five Security Gaps
1. Zero Input Validation
This was the most common issue. Over half of my projects had API endpoints that accepted whatever JSON you threw at them. No schema validation. No type checking. Just await request.json() and hope for the best.
That means any malformed request — or any intentionally crafted payload — gets processed by your business logic with zero guardrails. A missing field crashes your app. A wrong type corrupts your database. A malicious string does whatever it wants.
AI never added validation because I never asked for it. The endpoint worked with correct input, and that was good enough to pass the vibe check.
The fix: A validation library like Zod with a shared utility function. Something like parseBody(request, schema) that returns clean, typed data or a structured 400 error. Took about 30 minutes per project to retrofit across every route.
2. No Rate Limiting
Not a single project had rate limiting. Every endpoint — including payment flows, AI-powered features, and authentication routes — could be hammered indefinitely by anyone.
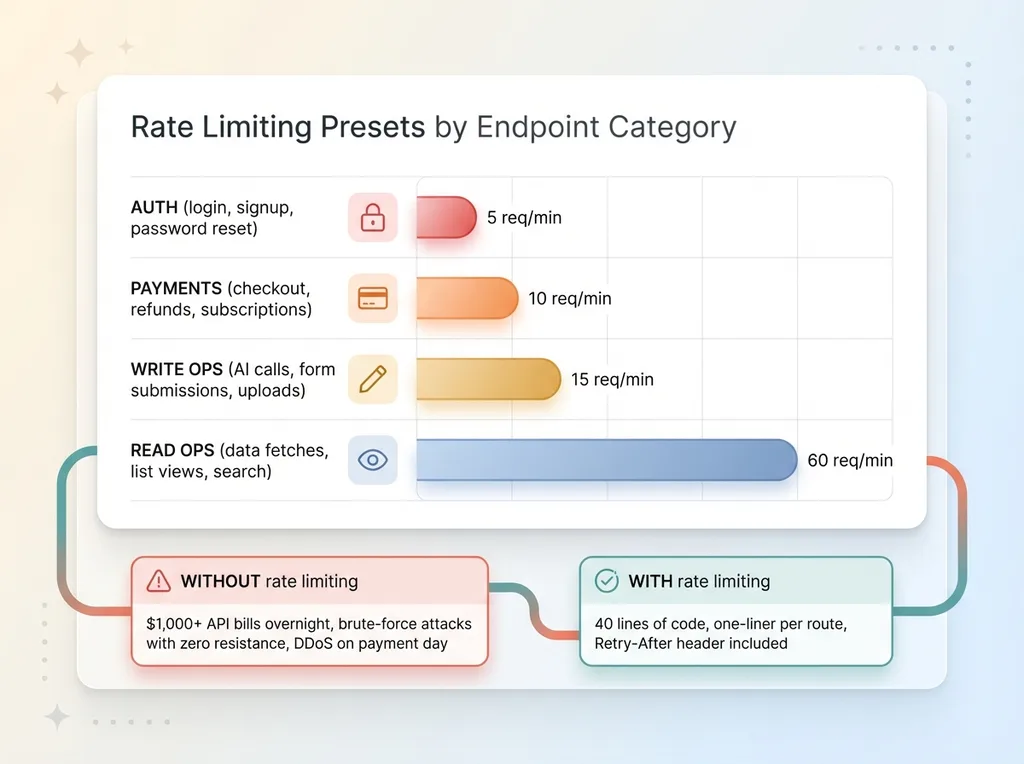 Rate Limiting Presets by Endpoint Type
Rate Limiting Presets by Endpoint Type
Think about what that means in practice:
- Someone triggers your AI endpoint a million times and your API bill hits four figures overnight
- A bot brute-forces your auth flow with zero resistance
- Your payment processing gets DDoS'd during your biggest sales day
The fix: An in-memory sliding window rate limiter with sensible presets. I used categories: 5 requests per minute for auth, 10 for payments, 15 for write operations, 60 for reads. The whole utility is about 40 lines of code, and wiring it into a route is a one-liner.
3. Missing Security Headers
None of my Next.js projects had security headers configured. No Content Security Policy. No HSTS. No X-Frame-Options. No referrer policy. No permissions policy.
This is the digital equivalent of leaving your front door unlocked. Clickjacking, MIME type confusion, protocol downgrade attacks — all preventable with a single headers() function in your config file. Every major web framework supports it. AI just never adds it unless you ask.
The fix: One function in next.config.ts that returns the full header suite for every route. Copy-paste across projects. Five minutes each.
4. Exposed Secrets and Missing .env.example Files
One project had a live API token hardcoded in a markdown file. Not in source code — in documentation. The kind of thing that happens when you're moving fast and asking AI to write handover notes or debug logs.
Several projects were also missing .env.example files, meaning any new developer (or future you, six months from now) has to read every file to figure out what environment variables are needed.
The fix: Regex-based secret scanning as part of the audit. Pattern matching for common key formats — Stripe, Shopify, Supabase, API tokens. Plus generating .env.example files with placeholder values for every project.
5. CI/CD Running with Full Permissions
Multiple GitHub Actions workflows had no explicit permissions block. That means they ran with the default token permissions — which includes write access to your repo contents, packages, and deployments.
One malicious dependency in your supply chain and that workflow token becomes a skeleton key to your entire repository.
The fix: Two lines of YAML. Add a permissions: block to every workflow with the minimum access it actually needs. Most only need contents: read.
The Plot Twist: AI Fixed What AI Missed
Here's the ironic part. The same AI tools that skipped these security basics also fixed all 29 issues — in a single afternoon.
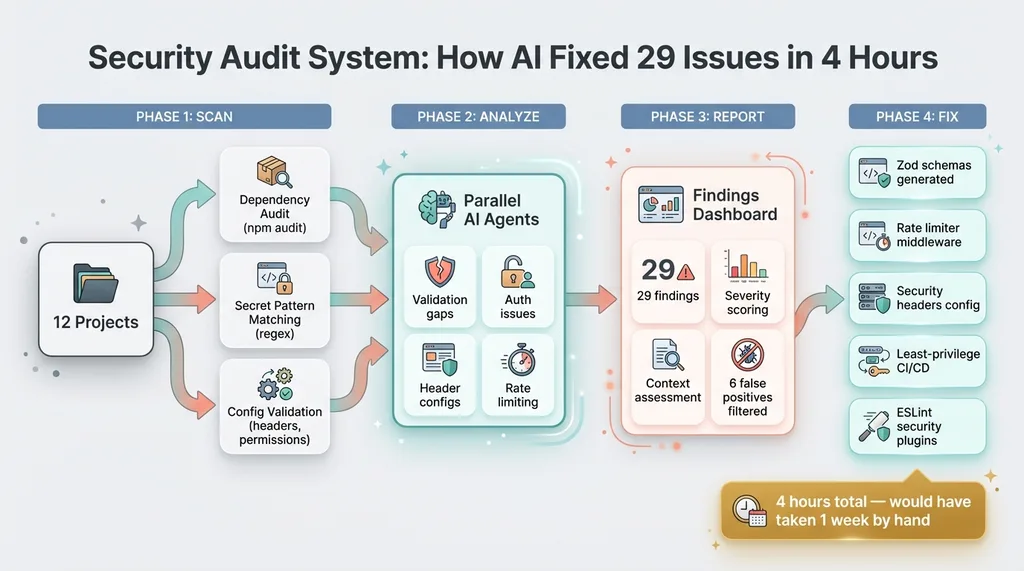 AI Security Scanning System Architecture
AI Security Scanning System Architecture
I built a security scanning system that:
- Runs automated checks across every project — dependency audits, secret pattern matching, config validation
- Launches parallel AI agents to deep-review code for validation gaps, auth issues, header configs, and rate limiting
- Tracks every finding with severity, status, and fix history
- Generates actionable reports I can work through systematically
The AI agents didn't just find the problems. They wrote the fixes:
- Zod schemas for every API route across multiple projects
- Rate limiting middleware with preset categories
- Security headers deployed to every Next.js app
- Least-privilege permissions on all GitHub Actions workflows
- ESLint security plugins for static analysis going forward
Total time: about 4 hours for the entire portfolio. By hand, that would have been a week of tedious, error-prone work.
Not Everything Is a Real Problem
An important lesson from this process: not every finding is a real vulnerability. Six of my 29 findings turned out to be false positives after deeper investigation.
For example, the scanner flagged a Cloudflare Worker for "no auth middleware" — but the project uses Cloudflare Access with JWT verification at the infrastructure level. No middleware file doesn't mean no authentication. It means authentication lives somewhere the scanner didn't look.
Another project got flagged for "no input validation on API routes" — but it turned out to have zero API routes. It's a pure frontend dashboard. No endpoints, no request bodies, nothing to validate.
This is why automated scanning is the starting point, not the finish line. Every finding needs a human (or a very thorough AI agent) to assess context before you start writing fixes.
The Vibe Coder's Security Checklist
If you're building with AI, run through this list for every project. I guarantee you'll find gaps.
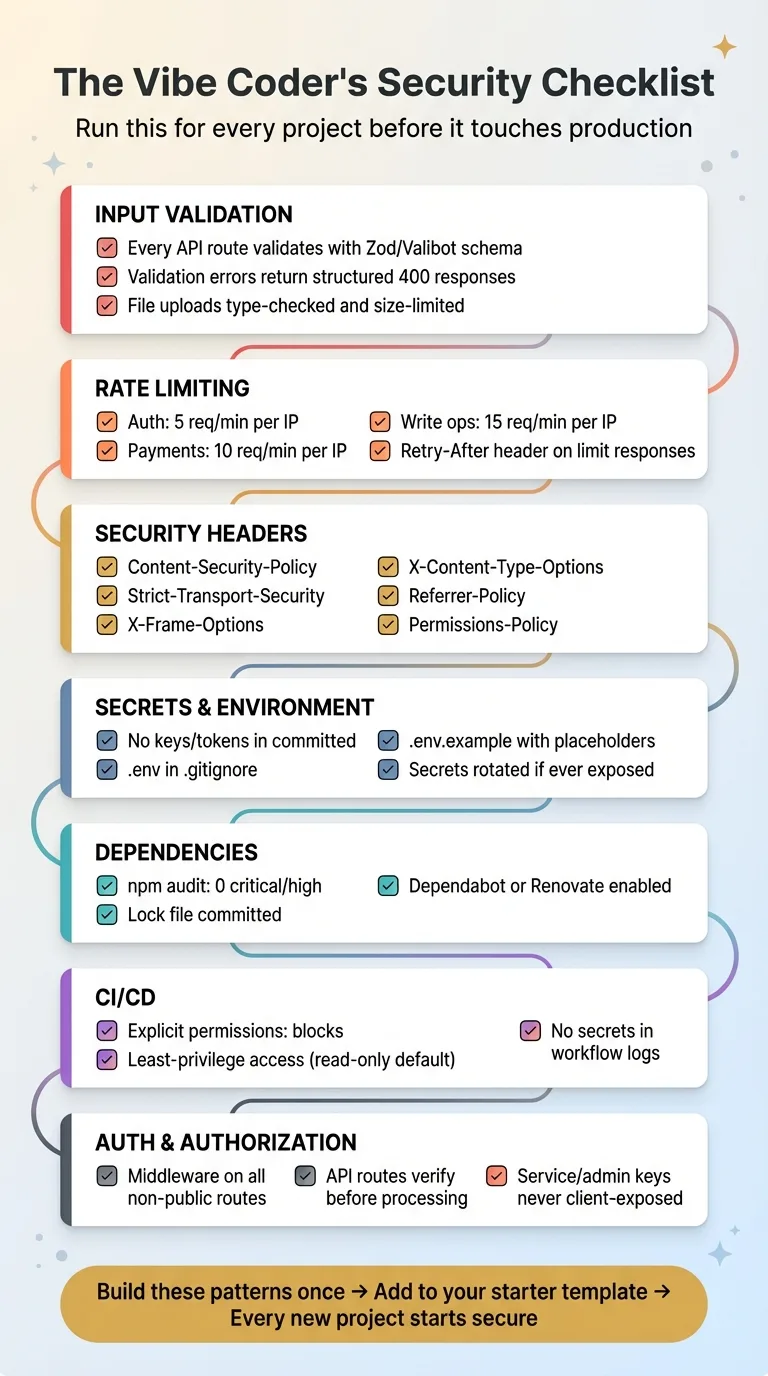 Vibe Coder's Security Checklist Overview
Vibe Coder's Security Checklist Overview
Input Validation
- Every API route validates its request body with a schema (Zod, Valibot, etc.)
- Validation errors return structured 400 responses, not stack traces
- File uploads are type-checked and size-limited
Rate Limiting
- Auth endpoints: 5 requests per minute per IP
- Payment endpoints: 10 requests per minute per IP
- Write endpoints (AI calls, forms, uploads): 15 requests per minute per IP
- Rate limit responses include a
Retry-Afterheader
Security Headers
- Content-Security-Policy (restrict where scripts, images, and frames load from)
- Strict-Transport-Security (force HTTPS)
- X-Frame-Options (prevent clickjacking)
- X-Content-Type-Options (prevent MIME sniffing)
- Referrer-Policy (control what gets sent in referer headers)
- Permissions-Policy (restrict browser features like camera and microphone)
Secrets & Environment
- No API keys, tokens, or passwords in committed files — including docs and READMEs
.envfiles are in.gitignore.env.exampleexists with placeholder values for every project- Secrets rotated if ever exposed, even in a private repo
Dependencies
npm auditreturns 0 critical and high vulnerabilities- Dependabot or Renovate enabled for automated updates
- Lock file committed (
package-lock.jsonorpnpm-lock.yaml)
CI/CD
- GitHub Actions workflows have explicit
permissions:blocks - Workflows use least-privilege access (read-only by default)
- No secrets exposed in workflow logs
Auth & Authorization
- Middleware protects all non-public routes
- API routes verify authentication before processing
- Service role and admin keys never exposed to the client
Build Fast, Then Lock the Doors
Vibe coding is the biggest unlock in software development since open source. I'm never going back to writing everything by hand. But speed without security is a liability — and the gap between "shipped" and "production-ready" is exactly these details.
The good news: once you build these patterns once, they're reusable. A validation utility, a rate limiter, a security headers config — these become part of your starter template. Every new project starts secure from line one.
AI helped me build 12 projects in record time. Then AI helped me secure all 12 in a single afternoon. That's the real power of this workflow: not just building fast, but building fast and building right.
If you're sitting on a portfolio of vibe-coded projects and you're not sure what's exposed, let's talk. I'll walk you through exactly what to look for — and how to fix it without slowing down.
Get AI insights for business leaders
Practical AI strategy from someone who built the systems — not just studied them. No spam, no fluff.
Ready to automate your growth?
Book a free 30-minute strategy call with Hodgen.AI.
Book a Strategy Call